
The following table shows current El Monte 30-year mortgage refinance rates. You can use the menus to select other loan durations, alter the loan amount, set your home value, select purchase loans, or change your location.
When purchasing a home, one of the most confusing aspects of the process is selecting a loan. There are many different financial products to choose from, each of which has advantages and disadvantages. The most popular mortgage product is the 30-year fixed rate mortgage (FRM).
This article discusses how the 30-year compares to other mortgage products, benefits of the 30-year, and fess to avoid when selecting a 30-year mortgage.
In recent years around 90% of borrowers used a 30-year FRM to purchase their home. The reason this loan is so popular is the certainty it offers coupled with the low rates.

Expert economists predicted the economy would rebound in 2010. However, the economy was sluggish with slow growth rates for many years beyond that. The economy contracted in the first quarter of 2014, but in the second half of 2014 economic growth picked up. The Federal Reserve tapered their quantitative easing asset purchase program & the price of oil fell sharply. Consumer perception of inflation and inflation expectations are set largely by the price they pay at the pump when they refill their gas. With growth picking up the consensus view is interest rates will continue to head higher for the next couple years into 2020, or until a recession happens. The following table highlights 2019 rate predictions from influential organizations in the real estate & mortgage markets.
| Organization | Analyst | Rate prediction |
|---|---|---|
| Freddie Mac | Actual PMMS 30-Year Rates | 3.94% |
| Mortgage Banker's Association | Mike Fratantoni | 5.1% |
| Fannie Mae | Doug Duncan | 4.8% |
| Freddie Mac | Sam Khater | 5.1% |
| Realtor.com | Danielle Hale | 5.3% |
| Moody's Analytics | Mark Zandi | 5.0% |
| Wells Fargo | Sam Bullard | 4.9% |
| Carrington Mortgage | Rick Sharga | 5.25% |
| CoreLogic | Frank Nothaft | 5.25% |
| National Association of Home Builders | 4.81% | |
| Zillow | 5.8% |
Table sources: MBA, Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, NAR, NAHB, CoreLogic
The NAHB saw 30-year fixed rates rising to 5.08% in 2020, when they anticipated ARMs to jump from 2019 estimates of 4.46% to 4.63%.
Despite being old data, the above predictions remain published on this page to show how significantly off major industry associations and leading experts at companies worth billions of dollars can be even in relatively benign environments. The average rate predicted for 2019 was 5.13% while the actual average rate throughout the year was 3.94%.
Industry experts can be that far off in relatively benign conditions. A true crisis can make accurate predictions nearly impossible.
As the COVID-19 healthcare crisis swept the globe governments pushed lockdowns which contracted many economies at record rates. In the second quarter of 2020 the United States economy contracted at a record annualized rate of 31.4%.
As the global economy crashed the Federal Reserve's FOMC cut interest rates twice, announced they would conduct unlimited quantitative easing, and gave forward guidance suggesting they were unlikely to lift rates through 2023.
As the Federal Reserve bought Treasury bonds and mortgage-backed securities while the economy cooled mortgage rates fell to new record lows. On the week of November 5th, the average 30-year fixed-rate fell to 2.78%. 2020 is expected to be a record year for mortgage originations with Fannie Mae predicting $4.1 trillion in originations and refinance loans contributing $2.7 to the total.
When selecting a mortgage, there are many different mortgage products and terms to choose from, each of which has different interest rates. While 30-year fixed rates are near an all-time low, and were recently below 4%, they are still higher than other loan options with a shorter duration. 30-year rates can be compared to the following popular products:

15-year Fixed Rates
15-year fixed rates are normally lower than a 30-year and, depending on the lender, the interest rate variance ranges from 0.50% to 0.75%. These rates are often lower because having a shorter term provides significantly less risk to the lender. Although interest rates are lower, 15-year payments are higher than 30-year payments because the loan has to be paid off in half the time.
Adjustable Rate Mortgages
An ARM typically comes with an interest rate slightly below those of a 30-year (though there has been a slight inversion in this relationship in the middle of 2020). With an ARM, a borrower receives a fixed interest rate for an introductory period of time, which normally ranges form 1 to 7 years, before the rate adjusts to reflect broader market conditions. Normally, the shorter the initial low interest period is, the lower the interest rate is. The most common ARM product is the 5-year Adjustable Rate Mortgage, which commonly comes with an interest rate that is typically 0.25% to 1% less than a 30-year. After the introductory period is up the loan's rate regularly adjusts every 6-months to year based upon a reference rate like the London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR) or the 11th district Cost of Funds Index (COFI). ARMs come with an interest rate cap, though this cap is typically significantly above the rates charged on FRMs.
Interest Only Mortgages
While they are not as frequently offered today as in years past, many borrowers still opt for interest only mortgages. Since interest only loans do not require principal payment and do not amortize, the balance due never decreases. Because of this, lenders assume a lot more risk and often require a sizable down payment and charge higher interest rates. Interest only mortgage rates are commonly 1% higher than 30-year rates.
The following graph shows historical data from the Freddie Mac Primary Mortgage Market Survey. It shows historical rate data back to 1971 for the 30-year, along with 15-year data back to 1991 and 5/1 ARM data from 2005 onward.
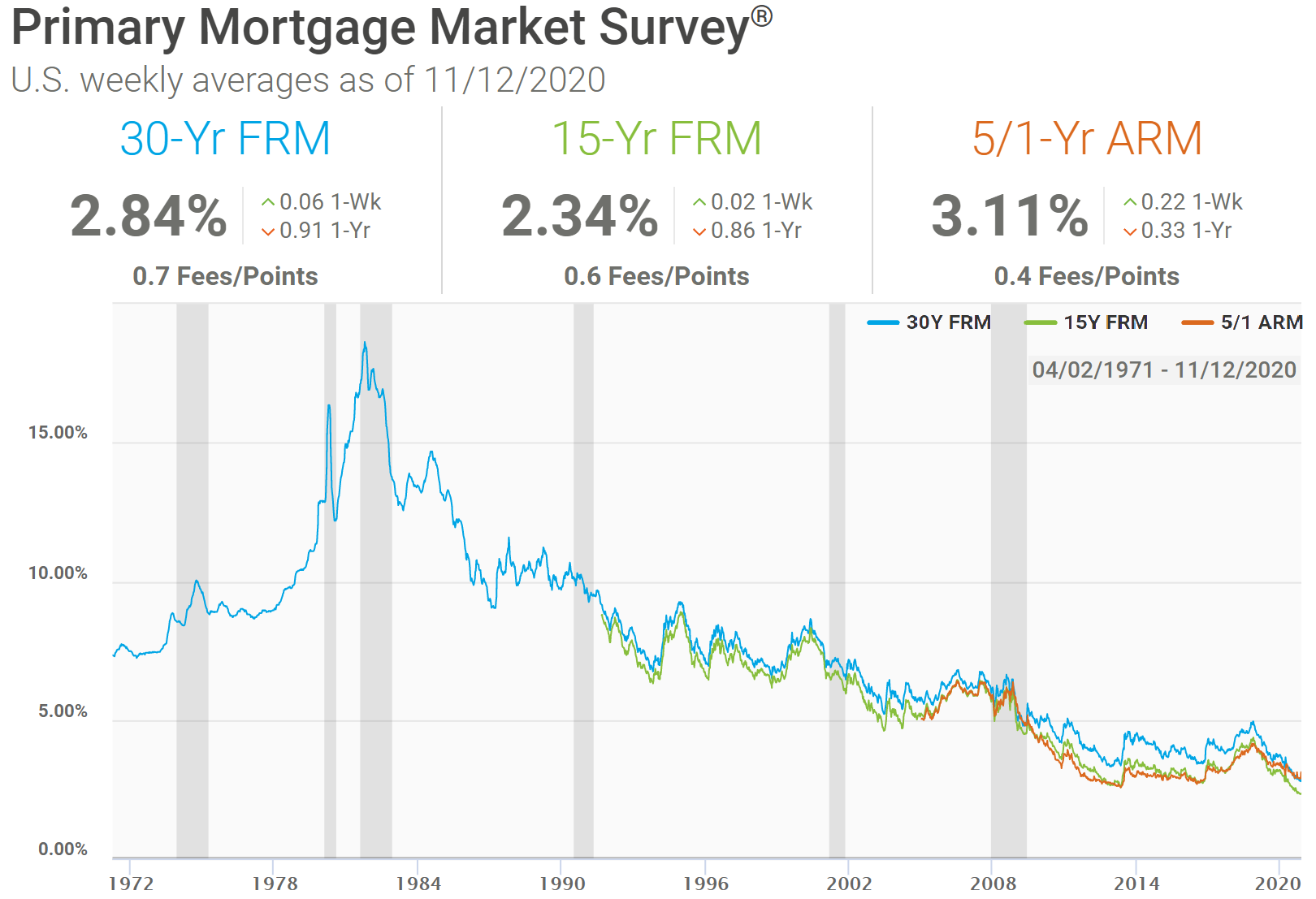
On August 15, 1971 President Nixon closed the gold window due to mounting costs of Great Society programs and the cost of the war in Vietnam.
Inflation soared into the early 1980s until Federal Reserve Chairman Paul Volcker lifted interest rates to engineer a recession and tame inflation. Since 1981 interest rates have been in a secular decline, and mortgage rates followed their trend. Typically the 30-year FRM tracks movements in the 10-year Treasury, trading at about a percent higher.

The best time to get a 30-year mortgage is when interest rates are low. Interest rates tend to fluctuate significantly over time. In late 2020 average 30-year rates were below 3%. Prior to the Great Recession rates were above 6% and were as high as 18.45% in October of 1981.
Rates depend on various economic factors, including the following:
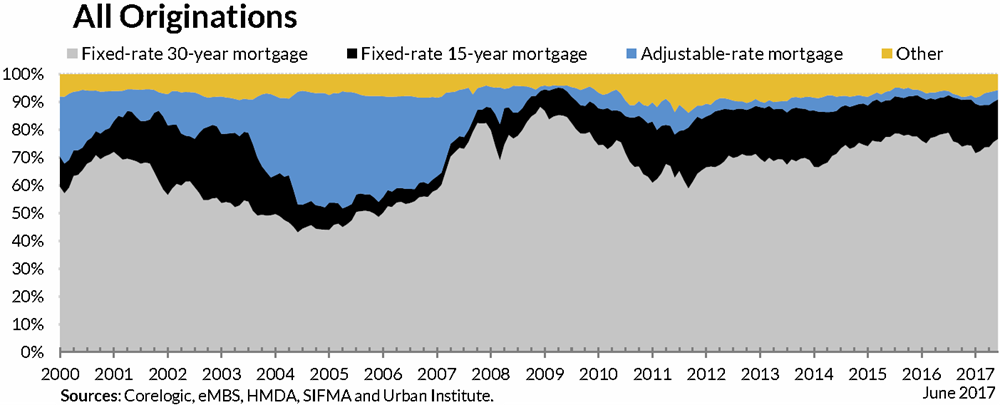
The 30-year FRM is easily the most popular choice among both home buyers and people choosing to refinance their home loans into a lower rate.
If one looks at the market as a whole, people using 15-year FRM to refinance makes the overall market composition look a bit more even than it would without refis.
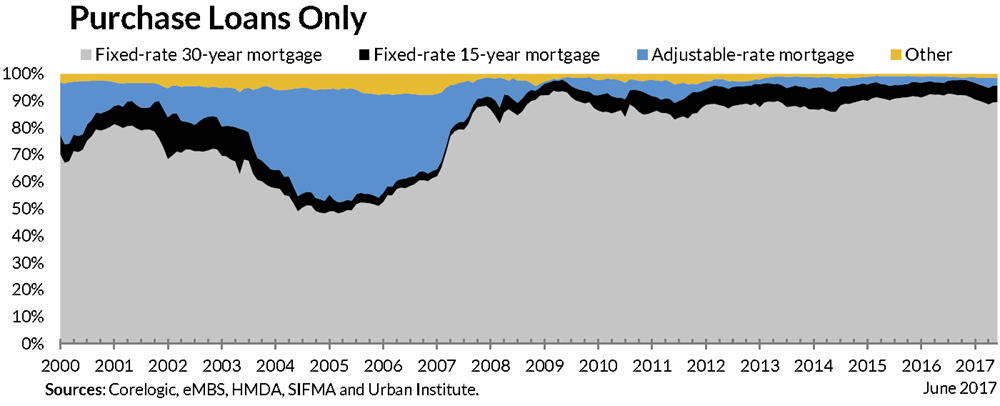
If one looks exclusively at purchases FRMs are about 90% of the market.

Compare 30 Year Fixed vs Other Loans
Estimate fixed monthly payments with this free calculator, or compare loans side by side.
Selecting a 30-year over other options comes with many benefits. Some of the benefits are:
While there are many benefits of selecting a 30-year, some lenders attempt to lump additional costs of fees into the mortgage. Paying closing costs is ultimately unavoidable, as you have to cover the bank's costs & those who tell you there are "no closing costs" typically roll these costs into the loan via a higher interest rate. Some of the most common costs or fees that borrowers should be aware of are as follows:
The Federal Reserve has begun lowering interest rates. Lock in today's low rates and save on your loan.
Are you paying too much for your mortgage?
Check your mortgage options with a trusted El Monte lender.
Answer a few questions below and connect with a lender who can help save you money today!